Physics 12 Field and Force
A magnetic field is a vector field in the neighbourhood of a magnet, electric current, or changing electric field in which magnetic forces are observable. A magnetic field is produced by moving electric charges and intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property known as spin.
Field Lines Definition, Properties, How to Draw Teachoo
Key terms Forces at a distance and fields Forces at a distance, such as gravitational, electric, and magnetic forces, can be represented using vector fields. These fields describe a relationship a given object might experience to the forces at any point in space. Fields are often represented in two dimensions using field lines.
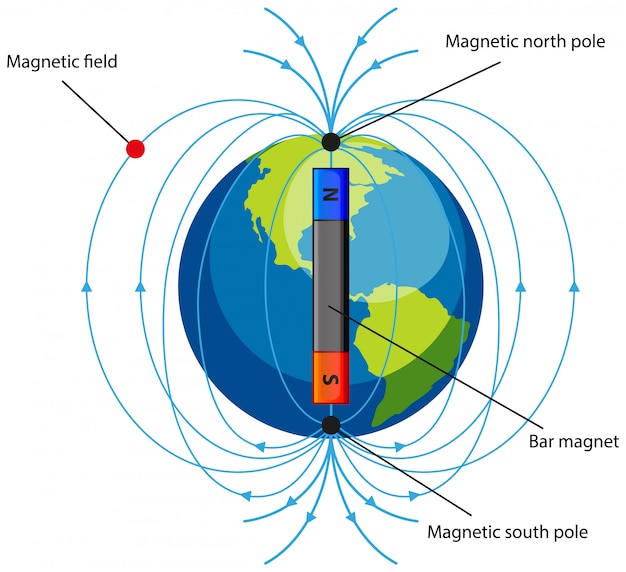
Diagram showing field on white Vector Free Download
In equations the magnitude of the magnetic field is given the symbol B . You may also see a quantity called the magnetic field strength which is given the symbol H . Both B and H have the same units, but H takes into account the effect of magnetic fields being concentrated by magnetic materials. For simple problems taking.
field — Science Learning Hub
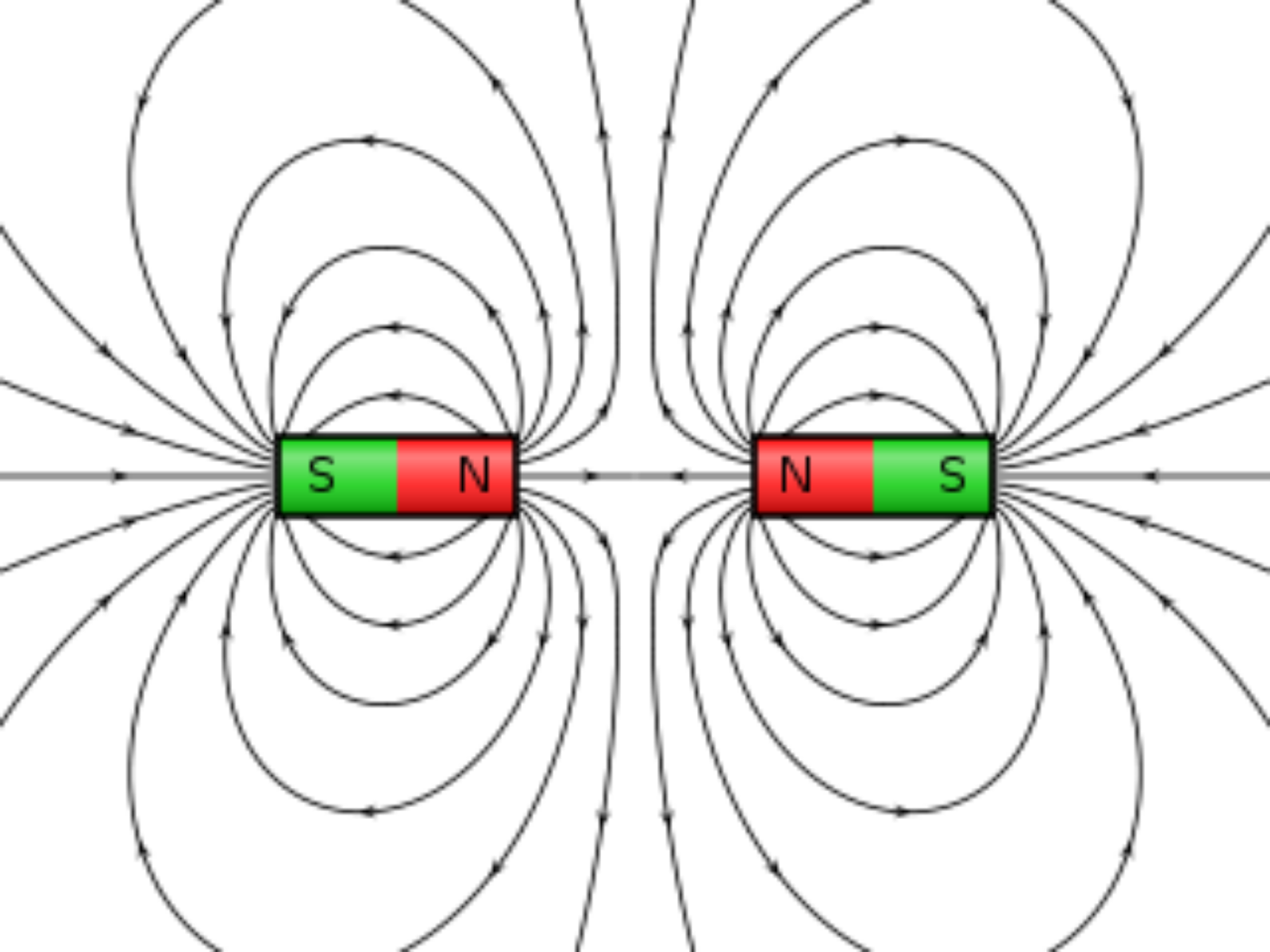
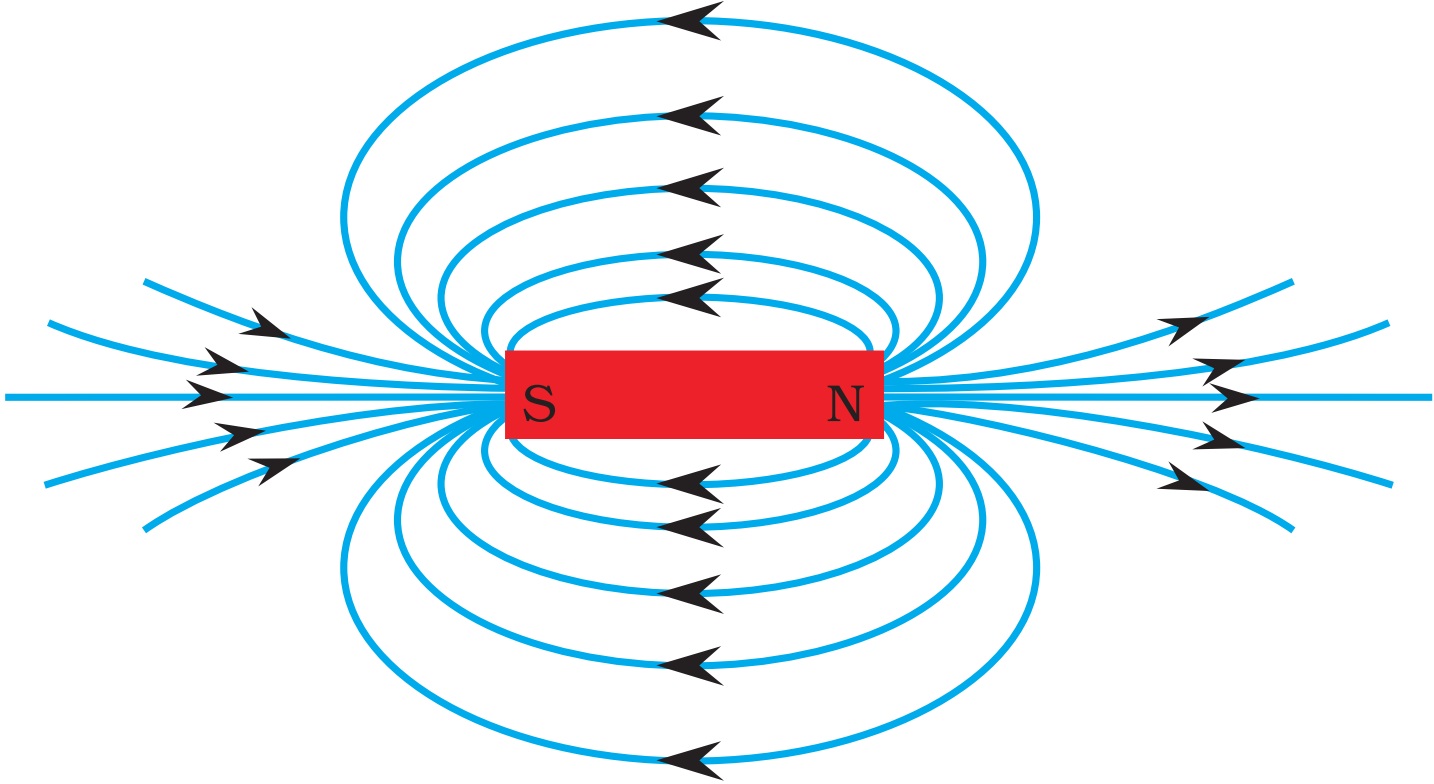
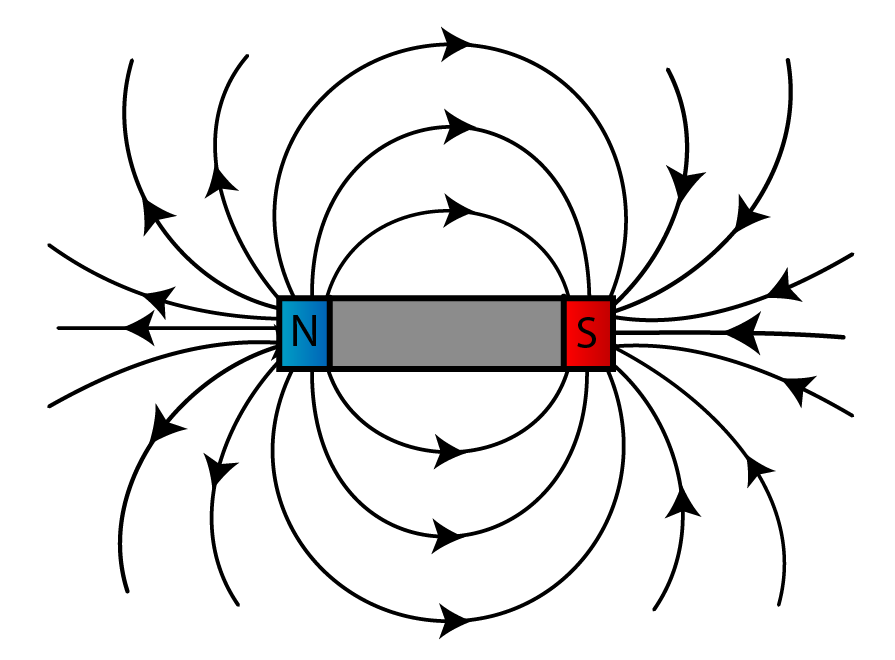
The diagram shows these key features: the magnetic field lines never cross each other the closer the lines, the stronger the magnetic field the lines have arrowheads to show the direction.

Lightning and the Sun's Field NaturPhilosophie
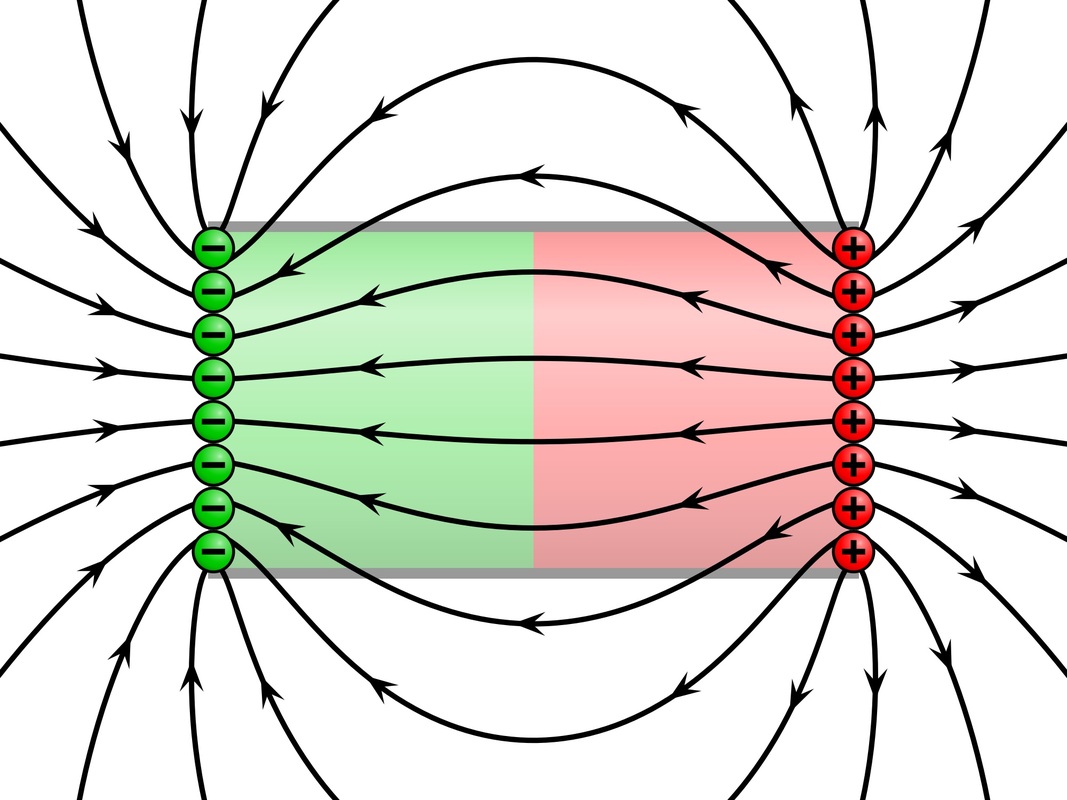
The magnetic field at a point is in the direction of the force a north pole of a magnet would experience if it were placed there. In other words, the north pole of a compass points in the direction of the magnetic field.. The following diagram shows the path followed by two charges, one positive and one negative, in a magnetic field that.

La Direction 333 2012 Pole Reversal Happens All The (Geologic) Time
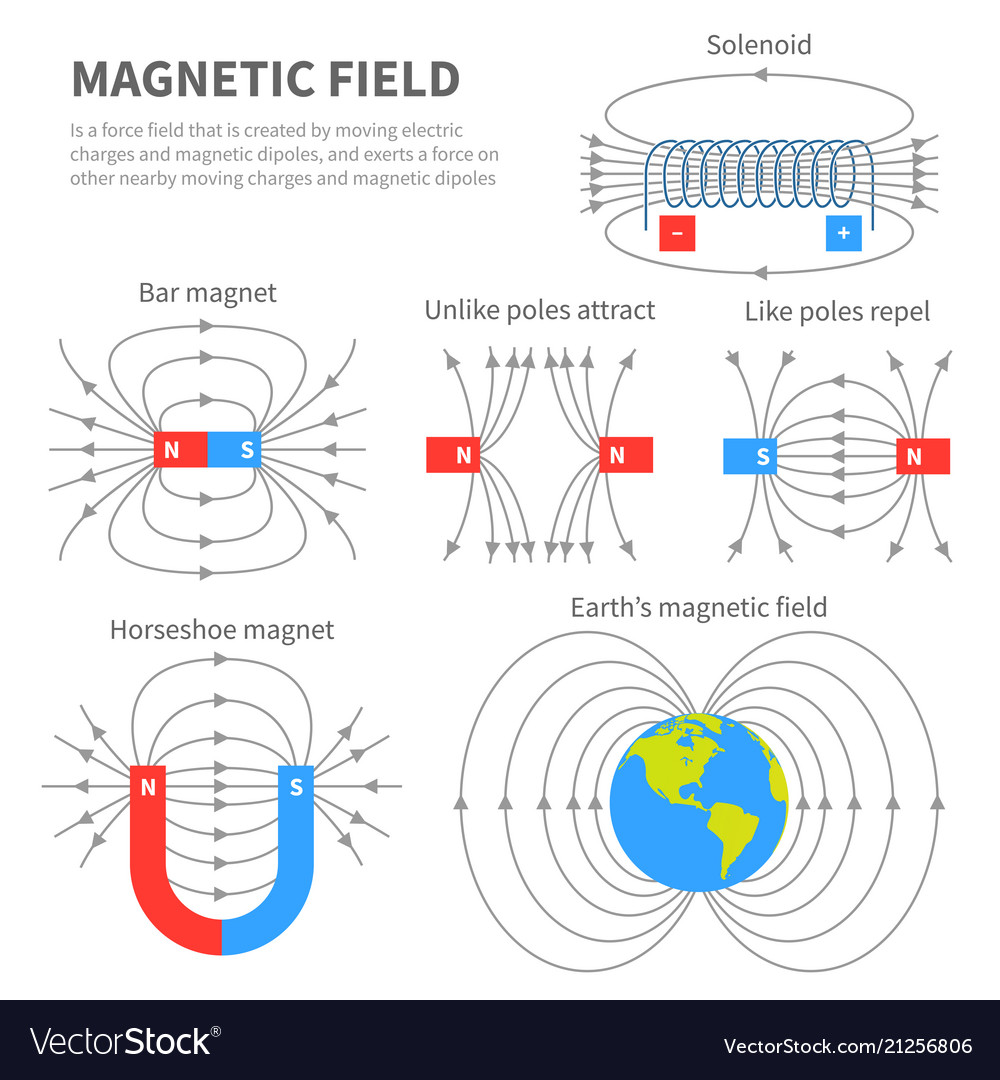
A magnetic pole is the part of a magnet that exerts the strongest force on other magnets or magnetic material, such as iron. For example, the poles of the bar magnet shown in Figure 20.2 are where the paper clips are concentrated. Figure 20.2 A bar magnet with paper clips attracted to the two poles.
Introduction to (Revision) SPM Physics Form 4/Form 5 Revision Notes
The magnetic field created by current following any path is the sum (or integral) of the fields due to segments along the path (magnitude and direction as for a straight wire), resulting in a general relationship between current and field known as Ampere's law. The magnetic field strength at the center of a circular loop is given by.
2 CLF Online Learning
The diagram shows a rigidly-clamped straight horizontal current-carrying wire held mid-way between the poles of a magnet on a top pan balance. The wire is perpendicular to the magnetic field direction. The balance, which was zeroed before the switch was closed, reads 112 g after the switch is

2. The field of a dipole in a rotating frame... Download Scientific
The magnetic force is directed where your thumb is pointing. If the charge was negative, reverse the direction found by these steps. Figure 11.3.1 11.3. 1: Magnetic fields exert forces on moving charges. The direction of the magnetic force on a moving charge is perpendicular to the plane formed by b v. ⃗.

NMR Using Earth’s Field Berkeley Lab
Magnetic field strength is also known as flux density. Its symbol is B and the unit is the tesla (T). With the current and magnetic field directions shown in the diagram below the force is into the paper. KEY POINT - The force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field is given by the expressions: when the conductor is perpendicular to.
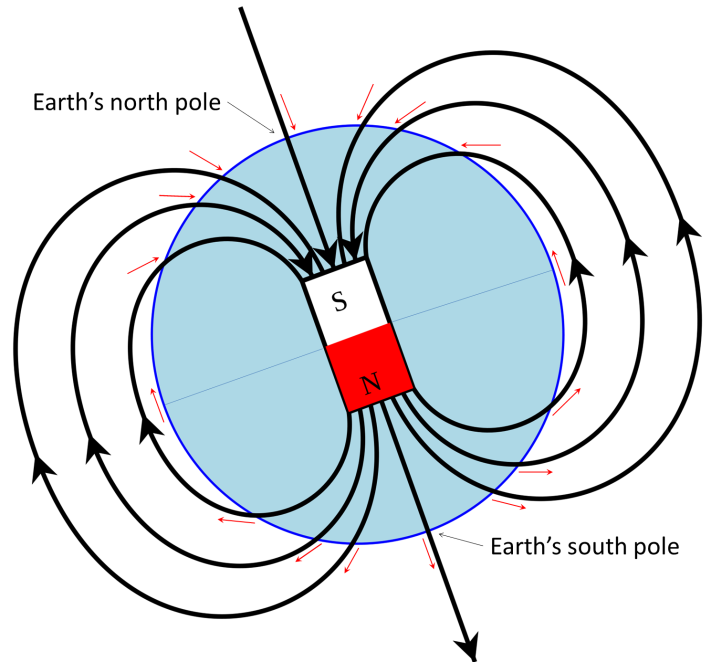
9.3 Earth’s Field Physical Geology
F = qvBsinθ F = q v B sin θ. 11.2. where θ is the angle between the velocity and the magnetic field. The SI unit for magnetic field strength B is called the tesla (T) after the eccentric but brilliant inventor Nikola Tesla (1856-1943), where. 1T = 1N A ⋅ m. 1 T = 1 N A · m.
Field Diagram
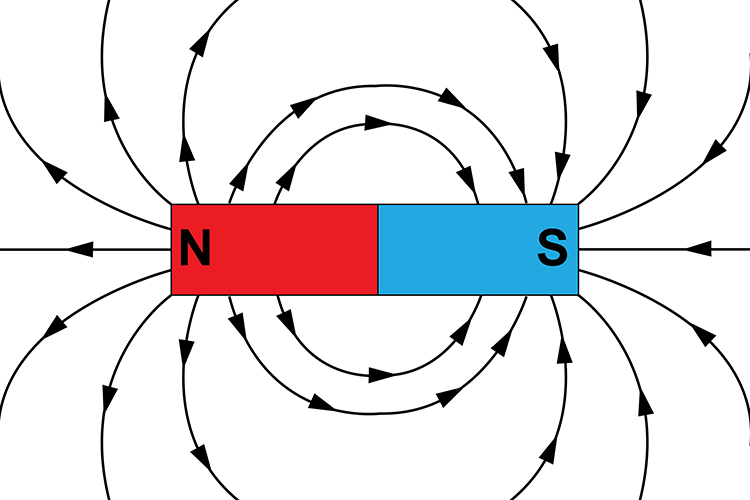
20.1 - Concept of a Magnetic Field. A magnetic field arises due to the relative motion of charges or from substances referred to as permanent magnets. Magnetic fields can be represented with field lines similar to the electric fields discussed previously. When drawing magnetic field lines, the convention for the direction is to go from north to.
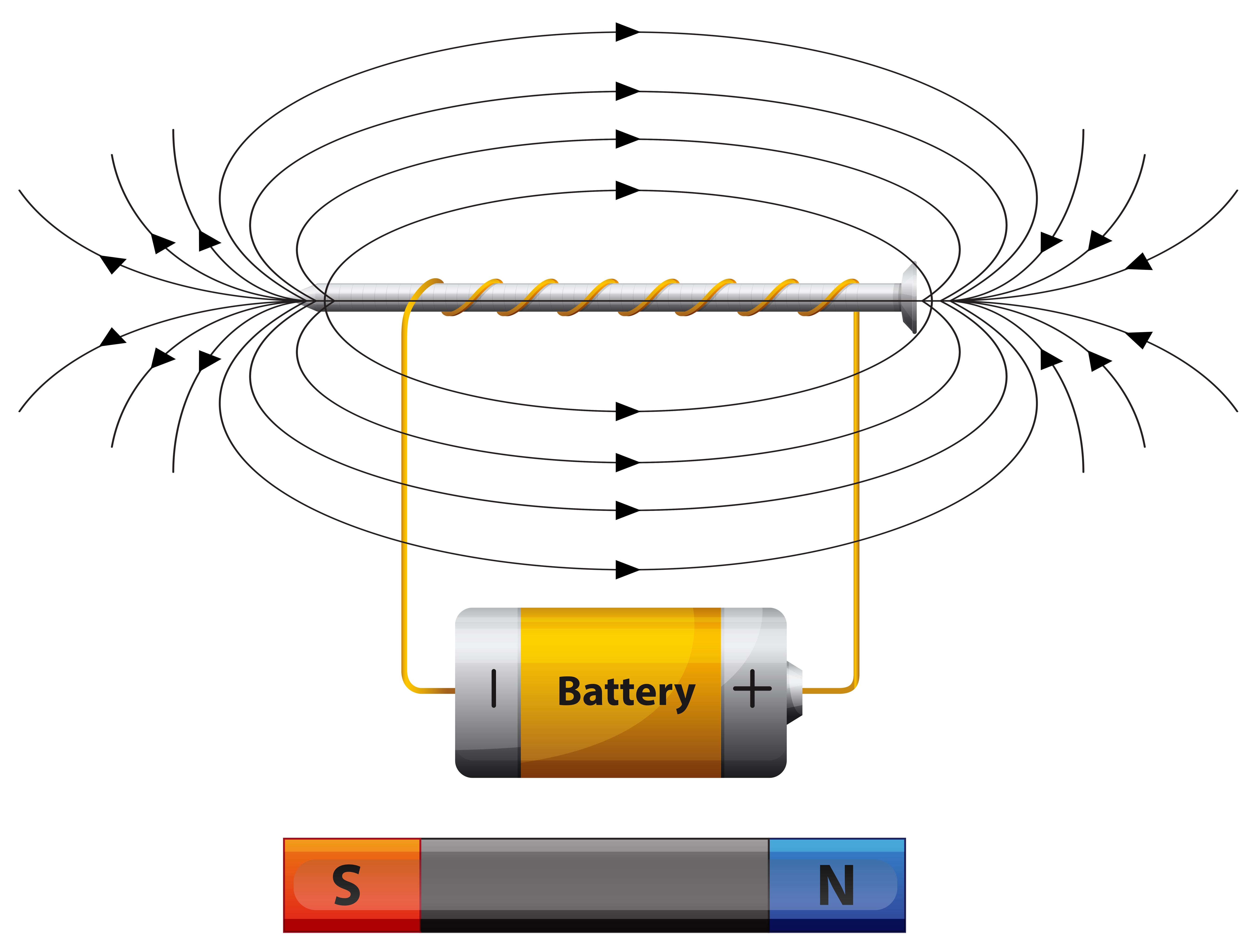
Diagram showing field with battery 448674 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Lesson 1: Magnetism of magnets and wires Intro to magnetic fields (Why fields?) Magnetic field lines: direction Magnetic field lines: special properties Magnetic field lines: field strength Science > Electromagnetism (Essentials) - Class 12th > Why are magnets magnetic? And why are other things not? > Magnetism of magnets and wires

Fields, Forces, & Effects Britannica
The diagram shows the magnetic field around a bar magnet. The diagram shows these key features: the magnetic field lines never cross each other the closer the lines, the stronger the.
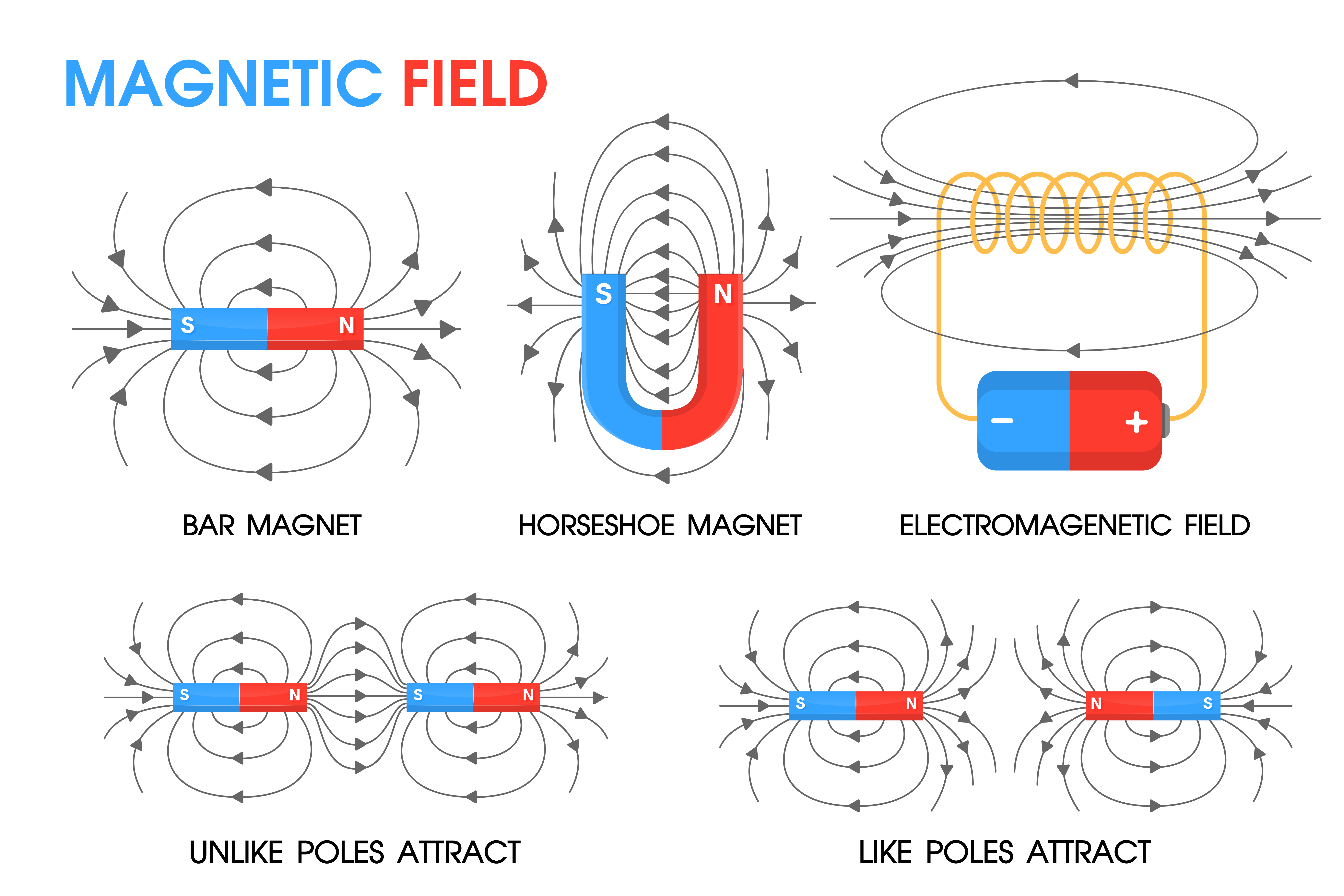
Physics science about the movement of fields Positive and negative. 593998 Vector Art
P7 A) Permanent Magnets. Magnets produce magnetics field, which is a region where another magnet or a magnetic material will experience a non-contact force (a force whereby objects do not need to be touching). Magnets have two poles; a north and a south pole. The north pole of a magnet is positively charged, and the south pole of a magnet is.

Diagram of field lines. Opposite poles attract, and like poles repel Stock Photo Alamy
The diagram shows these key features: the magnetic field lines close magnetic field line An imaginary line which indicates the direction of force caused by a magnet.